Decision making is the most important aspect of almost all the programming languages. As the name implies, decision making allows us to run a particular block of code for a particular decision. Here, the decisions are made on the validity of the particular conditions. Condition checking is the backbone of decision making.
In python, decision making is performed by the following statements.
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| If Statement | The if statement is used to test a specific condition. If the condition is true, a block of code (if-block) will be executed. |
| If – else Statement | The if-else statement is similar to if statement except the fact that, it also provides the block of the code for the false case of the condition to be checked. If the condition provided in the if statement is false, then the else statement will be executed. |
| Nested if Statement | Nested if statements enable us to use if ? else statement inside an outer if statement. |
Indentation in Python
For the ease of programming and to achieve simplicity, python doesn’t allow the use of parentheses for the block level code. In Python, indentation is used to declare a block. If two statements are at the same indentation level, then they are the part of the same block.
Generally, four spaces are given to indent the statements which are a typical amount of indentation in python.
Indentation is the most used part of the python language since it declares the block of code. All the statements of one block are intended at the same level indentation. We will see how the actual indentation takes place in decision making and other stuff in python.
The if statement
The if statement is used to test a particular condition and if the condition is true, it executes a block of code known as if-block. The condition of if statement can be any valid logical expression which can be either evaluated to true or false.
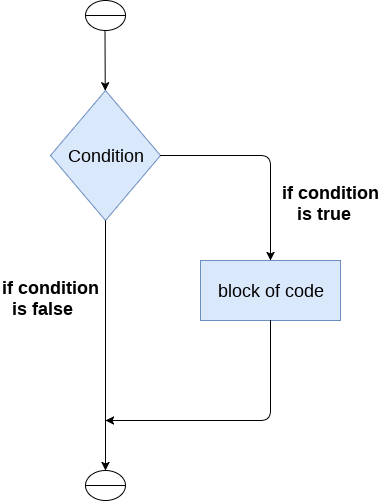
The syntax of the if-statement is given below.
ifexpression:
statement
Example 1
num = int(input("enter the number?"))
if num%2 == 0:
print("Number is even")
Output:
enter the number?10 Number is even
Example 2 : Program to print the largest of the three numbers.
a = int(input("Enter a? "));
b = int(input("Enter b? "));
c = int(input("Enter c? "));
if a>b and a>c:
print("a is largest");
if b>a and b>c:
print("b is largest");
if c>a and c>b:
print("c is largest");
Output:
Enter a? 100 Enter b? 120 Enter c? 130 c is largest
The if-else statement
The if-else statement provides an else block combined with the if statement which is executed in the false case of the condition.
If the condition is true, then the if-block is executed. Otherwise, the else-block is executed.
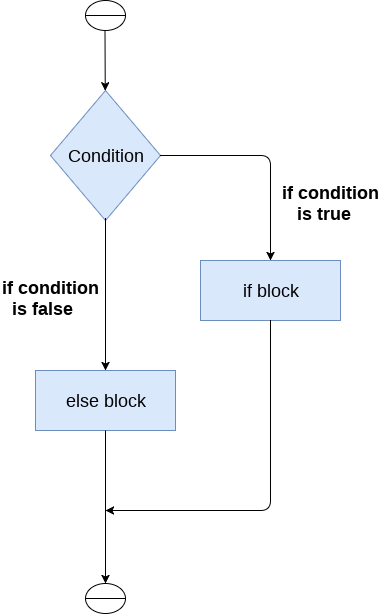
The syntax of the if-else statement is given below.
if expression 1:
# block of statements
elif expression 2:
# block of statements
elif expression 3:
# block of statements
else:
# block of statements
Example 1
number = int(input("Enter the number?"))
if number==10:
print("number is equals to 10")
elif number==50:
print("number is equal to 50");
elif number==100:
print("number is equal to 100");
else:
print("number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100");
Output:
Enter the number?15 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Example 2
marks = int(input("Enter the marks? "))
if marks > 85 and marks <= 100:
print("Congrats ! you scored grade A ...")
lif marks > 60 and marks <= 85:
print("You scored grade B + ...")
lif marks > 40 and marks <= 60:
print("You scored grade B ...")
lif (marks > 30 and marks <= 40):
print("You scored grade C ...")
else:
print("Sorry you are fail ?")
if condition:
#block of statements
else:
#another block of statements (else-block)
Example 1 : Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not.
age = int (input("Enter your age? "))
if age>=18:
print("You are eligible to vote !!");
else:
print("Sorry! you have to wait !!");
Output:
Enter your age? 90 You are eligible to vote !!
Example 2: Program to check whether a number is even or not.
num = int(input("enter the number?"))
if num%2 == 0:
print("Number is even...")
else:
print("Number is odd...")
Output:
enter the number?10 Number is even
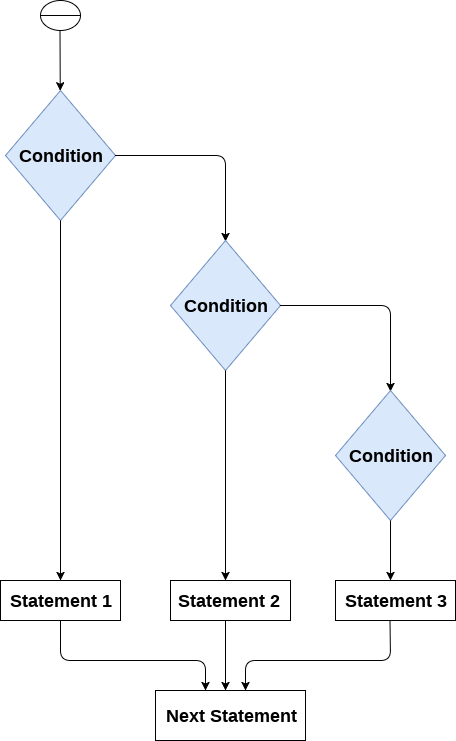
The elif statement
The elif statement enables us to check multiple conditions and execute the specific block of statements depending upon the true condition among them. We can have any number of elif statements in our program depending upon our need. However, using elif is optional.
The elif statement works like an if-else-if ladder statement in C. It must be succeeded by an if statement.
The syntax of the elif statement is given below.
if expression 1:
# block of statements
elif expression 2:
# block of statements
elif expression 3:
# block of statements
else:
# block of statements

Example 1
elif number==50:
print("number is equal to 50");
elif number==100:
print("number is equal to 100");
else:
print("number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100"</span>);
Output:
Enter the number?15 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Example 2
marks = int(input("Enter the marks? "))
f marks > 85 and marks <= 100:
print("Congrats ! you scored grade A ...")
lif marks > 60 and marks <= 85:
print("You scored grade B + ...")
lif marks > 40 and marks <= 60:
print("You scored grade B ...")
lif (marks > 30 and marks <= 40):
print("You scored grade C ...")
lse:
print("Sorry you are fail ?")
